Thoracic/chest Cancer
Thoracic or chest cancer refers to cancer that develops in the organs and tissues
within the chest cavity, primarily affecting the lungs, heart, and other structures
like the esophagus. Lung cancer is the most common type of chest cancer, with
two main types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer
(SCLC). These cancers can cause symptoms such as persistent cough, chest pain,
shortness of breath, and unexplained weight loss. Risk factors include smoking,
exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollution, and occupational hazards like
asbestos.
Other cancers, such as esophageal cancer, can also develop in the chest
area, often leading to difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, or severe weight loss.
Early-stage chest cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms, making regular
screenings and early detection critical. Treatment varies depending on the type,
stage, and location of the cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy,
radiation therapy, or targeted therapies. Lung cancer, in particular, has a lower
survival rate when diagnosed in later stages, emphasizing the importance of
preventive measures and early diagnosis.
Types of Thoracic Cancer
1. Lung Cancer- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common type, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): A more aggressive form, often linked to smoking.
- Includes squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, depending on the type of cells affected.
- Arises from the thymus gland; includes thymoma and thymic carcinoma.
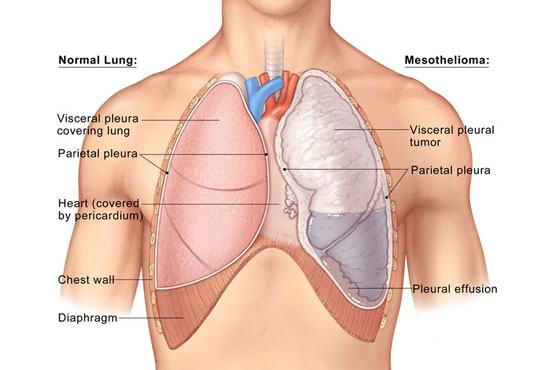
- Mesothelioma: Cancer of the pleura, often linked to asbestos exposure.
- Includes primary or metastatic tumors of the bones, muscles, or cartilage in the chest wall.
2. Esophageal Cancer
3. Thymic Cancer
4. Pleural Cancer
5. Chest Wall Tumors
Causes and Risk Factors
- Smoking: The leading cause of lung and some esophageal cancers.
- Environmental Exposures: Radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution.
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of thoracic cancers.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic acid reflux (linked to esophageal cancer) or autoimmune disorders (linked to thymic cancer).
Symptoms
Symptoms of thoracic cancer vary based on its type and stage but may include:
- Persistent cough or changes in a chronic cough.
- Chest pain or discomfort.
- Shortness of breath or wheezing.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Hoarseness or difficulty speaking.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
- Fatigue or weakness.
- Swelling in the face, neck, or arms (superior vena cava syndrome)

Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis often involves:
Treatment Options
1. Surgery2. Radiation Therapy
3. Chemotherapy
4. Targeted Therapy
5. Immunotherapy
6. Palliative Care
Prevention
- Quit Smoking: Most effective way to lower risk.
- Healthy Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Particularly for esophageal cancer prevention.
- Protect Against Carcinogens: Avoid exposure to radon, asbestos, and pollution.
- Regular Checkups: Especially for individuals with a family history or high-risk factors.
Treatment
Gastrointestinal Cancers
Gastrointestinal Cancers spreads to nearby organs and blood vessels.
Read MoreHead And Neck Cancer
One to two percent of cases of pancreatic cancer are neuroendocrine tumors.
Read More