Gynaecological Cancer
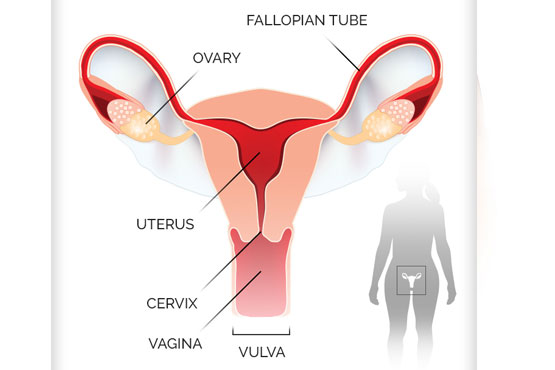
Gynaecological cancer refers to cancers that affect the female reproductive
system, including the ovaries, uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, vulva, and vagina.
The most common types are ovarian, uterine, cervical, and vaginal cancer, each
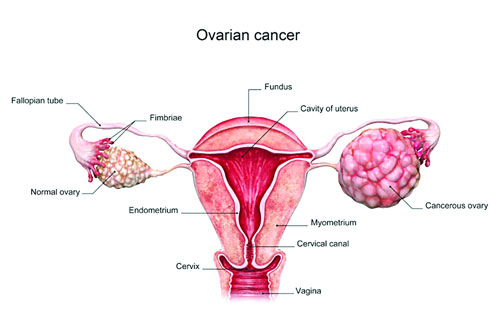
with distinct symptoms and risk factors. Ovarian cancer often remains
undiagnosed until it reaches advanced stages, with symptoms like bloating,
abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits.
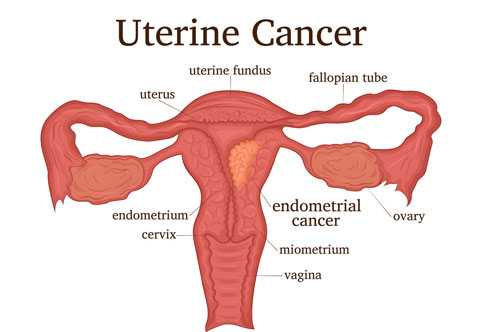
Uterine cancer typically causes
abnormal vaginal bleeding, particularly after menopause, and is more common in
women with certain risk factors, such as obesity and hormonal imbalances.
Cervical cancer is usually linked to persistent infection with high-risk strains of
human papillomavirus (HPV), and it often causes abnormal vaginal bleeding or
discharge. Risk factors for gynaecological cancers include family history, age, and
lifestyle factors like smoking and obesity. Early detection through regular
screening, such as Pap smears for cervical cancer, plays a crucial role in improving
treatment outcomes. Treatment options for gynaecological cancer depend on the
type and stage and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or
targeted treatments. Advances in early detection and treatment have improved
survival rates, especially when the cancer is diagnosed in its early stages.
Types of Gynaecological Cancer
1. Cervical Cancer- Originates in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus.
- Commonly caused by persistent infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Develops in the ovaries, responsible for producing eggs.
- Includes epithelial, germ cell, and stromal cell cancers.
- Starts in the lining of the uterus (endometrium).
- Often linked to hormonal imbalances.
- Rare cancer that begins in the vaginal lining.
- Affects the external genitalia, primarily the vulva.
- Extremely rare and usually associated with ovarian cancer.
2. Ovarian Cancer
3. Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
4. Vaginal Cancer
5. Vulvar Cancer
6. Fallopian Tube Cancer
Causes and Risk Factors
1. General Risk Factors2. Specific Risk Factors

Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the type and stage of cancer but may include:
1. Cervical Cancer:2. Ovarian Cancer:
3. Endometrial Cancer:
4. Vaginal and Vulvar Cancer:
Diagnosis
1. Screening and Early Detection2. Diagnostic Tests
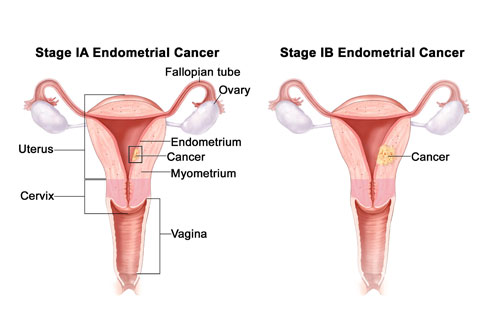
Staging of Gynaecological Cancer
Cancer staging determines the extent of the disease:

Prevention
1. Vaccination and Screening- HPV Vaccine: Protects against high-risk HPV strains.
- Regular Pap smears and HPV tests. 2. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption. 3. Genetic Counseling
- For women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer. 4. Awareness of Symptoms
- Early detection is key to better outcomes.
Treatment
Gastrointestinal Cancers
Gastrointestinal Cancers spreads to nearby organs and blood vessels.
Read MoreHead And Neck Cancer
One to two percent of cases of pancreatic cancer are neuroendocrine tumors.
Read More